Agricultural industry is going through the digital revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is assisting farmers to make quicker, smarter and more sustainable decisions, whether it is precision irrigation, monitoring crop health, or other purposes. However, in spite of all the mighty AI models in the field of agriculture, there is one key ingredient annotated data.
Here we will discuss the power of annotated data to drive AI-enabled agriculture and reasons why it has become the basis of the new agriculture.
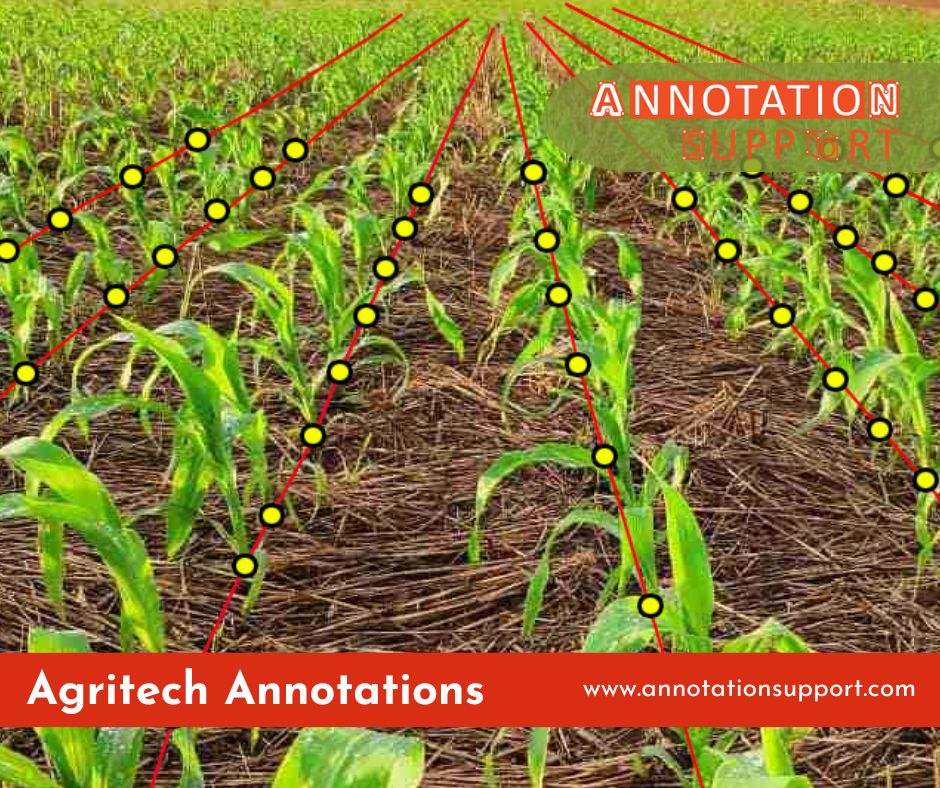
What Is the Data Annotation in Agriculture?
Annotated data: This type of data may be images, videos, or sensor data that has been annotated or tagged to specify particular objects – such as diseased leaves, pest infestations, soil types or crop boundaries.
This data in agricultural AI conditions trained machine learning models to identify, distinguish, and infer real-life farm situations with accuracy.
Examples include:
- Tagging satellite or drone pictures in order to determine types of crops.
- Labeling plant disease symptoms to be used in early detection.
- Labeling the weeds and crop to be sprayed automatically.
Why Annotated Data Matters in Smart Farming?
The AI systems in agriculture are also no smarter than the information that they are taught. The machine vision systems will not be able to differentiate between the healthy crops and the diseased ones or detect the weeds precisely without proper annotations.
This is the way in which annotated data would enhance intelligent farming activities:
1.Precision Crop Monitoring
Categorized under drone and satellite photography, AI-powered technology can monitor the state of crops, determine their growth potential, and help in identifying such conditions as nutrient deficiencies or attacks by pests in situ.
2.Automated Weed and Pest Detection
With the assistance of annotation services, models are able to detect various weed species or infestations of pests. This allows spraying specifically — lessening the use of chemicals and safeguarding of the soil.
3. Soil and Irrigation Management
The annotated soil data (moisture, pH, fertility levels) is used to suggest the irrigation schedule or fertilizers application to the AI to enhance the efficiency of water and resources.
4.Harvest forecasting and Yield forecasting
Plant stage labeling is beneficial as AI is capable of predicting the harvest and creating harvest schedules more effectively.
5.Livestock Monitoring
Animals Annotated video data is useful in animal farming where it assists in health monitoring, behavioural examination, and even in the early detection of disease in animals.
Building Agricultural AI Models: The Role of Data Annotation Services
Annotating farm data is a complicated task. It requires:
- Knowledge of the field (and what happens in the plant world, or the soil science)
- Detailed data of high quality (drone, satellite, or IoT sensors images).
- Advanced annotation tools (for bounding boxes, segmentation, or keypoint marking)
The data annotation providers advertise the accuracy and scalability of agricultural data by collaborating with agritech companies to work on agricultural datasets.
The Future: Feeding the World with Data-Driven Agriculture
With the growing demand of food in the world, AI powered farming is becoming essential in efficiency, sustainability, and productivity. These innovations are powered by annotated data – transform a raw image or numbers to use.
Annotated farm data not only fills the machines with food, but it is also the food of tomorrow to agriculture: agriculture-based AI is being used to predict harvest yields, combat the effects of climate change, among other uses.
Key Takeaway: Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture begins with data – and develops when it is properly annotated. The smarter the farm is the better the data is.
