Exploring the Top 5 Challenges in Annotating 3D Point Cloud Data from LIDAR: Solutions and Best Practices
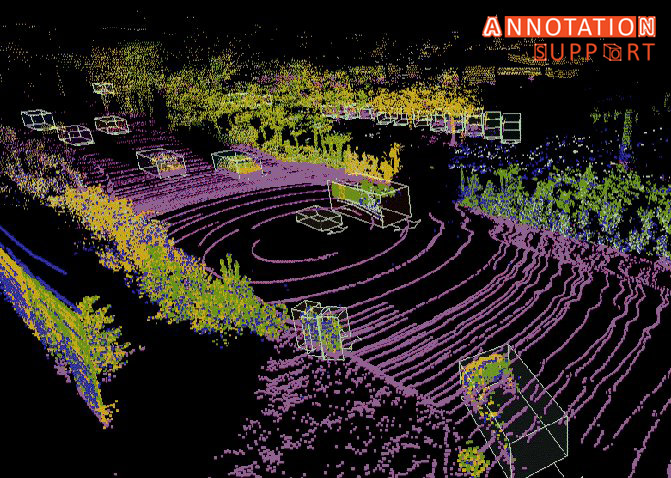
The LIDAR ( Light Detection and Ranging ) technology has become one of the foundations of a number of advanced technologies, including autonomous driving and robotics, smart cities and forestry management. The main importance of using LIDAR is its 3D point cloud data annotation, making it possible to teach the machine learning models to understand the real world in a three-dimensional format. Nevertheless, there are peculiar difficulties related to annotating 3D point clouds. In this case we would look at the 5 most common problems and suggest an effective solution or best practice that can help deal with them. 1. High Complexity and Volume of Data Challenge: The file size of 3D point clouds could be millions of points that reflect a complex environment with detail structure. Such dense datasets are hard to work with which makes annotators slow and prone to making errors. Solutions & Best Practices: 2. Poor Standardised Protocols of Annotation Challenge: In contrast to 2D image annotation, the 3D point cloud labelling has no common standards and leads to such issues as inconsistency and reduced dataset quality. Solutions & Best Practices: 3. Difficulty in Identifying Objects in Sparse or Occluded Areas Challenge: There are areas that lack point clouds or there are obstacles that hamper object identification and assigning labels to the objects unambiguously. Solutions & Best Practices: Multi-Sensor Fusion: Combine LIDAR data with camera images or radar to get complementary information. High-tech visualization: Work with tools where varying the point density of visualization and shift of viewpoint is possible. Contextual Labelling: Text annotations need to make use of context in a scene to deduce objects which are not visible. 4. Time-Consuming and Labor-Intensive Process Challenge: Labelling of 3D point clouds requires manual annotation that is more time-consuming compared to the 2D image annotation, which makes projects costlier and time-consuming. Solutions and best practices: Semi-Automatic Annotation: Use AI-based tools to tag the data in advance and then leave it to the annotators to fix the data in a short time. Active Learning: Model-in-the-loop based methods can be used in which the model proposes annotations to be verified by a human. Effective Design of the Workflow: Apply annotation workflows and reduce repetitive procedures and operations. 5. Handling Dynamic and Moving Objects Challenge: During high level uses such as autonomous driving, the objects change position between the frames of LIDAR, which makes it difficult to annotate the object related to a temporal sequence and tracking. Solutions and best practices: Conclusion It is important to annotate LIDAR-derived 3D point clouds data although it is a difficult task. With the introduction of standardized protocols, the use of advanced tools and AI support, multi-sensor data overlay, organizations will be able to raise the quality and efficiency of annotations by several orders of magnitude. All these are the best practices that can lead to the maximization of the possibility of the 3D LIDAR data into different innovative uses.